Comparison with Other Cheese Types: 1 Slice Of American Cheese Nutrition Facts
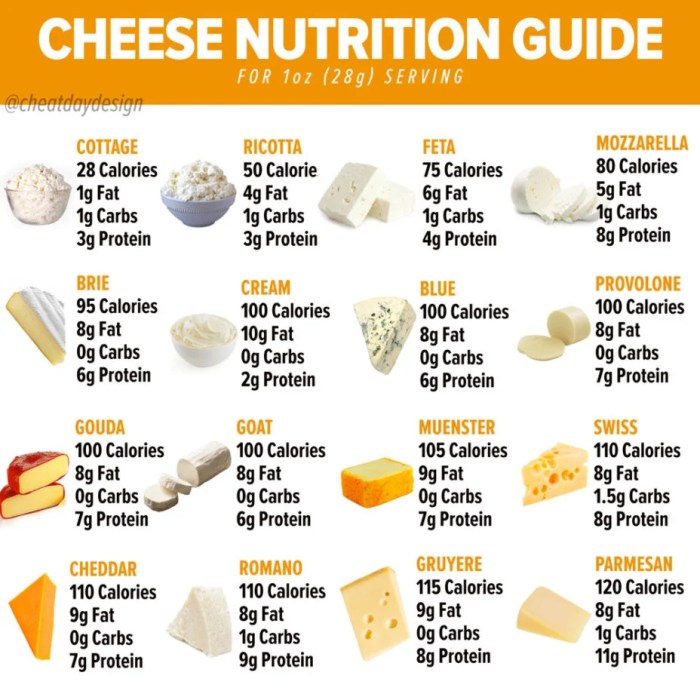
1 slice of american cheese nutrition facts – Yo, so we’re already checked out the nutritional facts for one slice of American cheese, right? Now let’s see how it stacks up against other popular cheese choices—Cheddar, Mozzarella, and Swiss. We’re gonna break down the fat, protein, sodium, and vitamin/mineral differences, Surabaya style. Think of it as a cheese showdown!
Comparing these cheeses helps us understand the nutritional variations and make informed choices based on our dietary needs and preferences. Different cheeses offer different nutritional profiles, impacting calorie intake, macronutrient balance, and micronutrient supply.
Nutritional Differences Among Cheese Types
Here’s the lowdown on how one slice of American cheese compares to its rivals in terms of fat, protein, and sodium. Remember, these are approximate values and can vary depending on the brand and type of cheese.
- Fat: American cheese is generally lower in fat than Cheddar, but higher than Mozzarella and often similar to Swiss. Cheddar packs a serious fat punch, while Mozzarella is surprisingly lighter. Swiss sits somewhere in the middle.
- Protein: All four cheeses are pretty similar in protein content per slice. It’s not a huge difference-maker when choosing between them based solely on protein.
- Sodium: This is where things get interesting. American cheese often has a higher sodium content than Cheddar, Mozzarella, and Swiss. If you’re watching your salt intake, you might want to consider those other options.
Vitamin and Mineral Content Comparison
Beyond the basics, let’s talk vitamins and minerals. While all these cheeses offer some nutritional benefits, their profiles differ slightly.
- Calcium: All four cheeses are good sources of calcium, essential for strong bones. The differences in amounts are usually minor.
- Vitamin A: Cheddar often boasts higher levels of Vitamin A compared to American, Mozzarella, and Swiss cheese.
- Vitamin B12: All these cheeses are good sources of Vitamin B12, crucial for nerve function and red blood cell formation. Again, the differences are usually not drastic.
Impact of Processing on Nutritional Value

Yo, peeps! Let’s get real about American cheese. It’s not exactly the same as that artisanal cheddar youremak* might bring home from the pasar. The processing it goes through seriously changes its nutritional game. We’re talking about the stuff that melts perfectly on your burger, not the fancy stuff.American cheese’s manufacturing process is, well,processed*. It starts with different cheeses, often cheddar, but also other kinds, being blended together.
Then, it’s heated, emulsifiers are added (think of them as the glue that holds it all together), and sometimes other ingredients like salt, colorings, and preservatives are thrown in. This process alters the cheese’s original structure and nutritional makeup. The heating process can denature some proteins, impacting digestibility and potentially reducing the bioavailability of certain nutrients. The addition of emulsifiers can also affect the cheese’s texture and fat content.
Understanding the nutritional breakdown of a single slice of American cheese is crucial for mindful eating. Think about the impact of adding that cheese to a slice of pizza – the caloric and fat content significantly increases! To fully grasp the nutritional implications, explore the details of slice cheese pizza nutrition and compare it to your baseline knowledge of that single slice of American cheese.
This comparison will empower you to make informed choices about your daily intake.
Compared to unprocessed cheeses, American cheese generally has a higher sodium content and lower levels of certain vitamins and minerals due to the processing steps and added ingredients.
Additives and Preservatives in American Cheese
American cheese often contains additives like emulsifiers (like sodium citrate or disodium phosphate), which help create that smooth, melty texture. Preservatives, like sodium propionate or sorbic acid, are added to extend shelf life. While these additives are generally considered safe within regulated limits, they don’t exactly boost the nutritional value. In fact, some might argue that excessive sodium intake from these additives can contribute to health issues like high blood pressure.
Colorings are sometimes used to give the cheese that characteristic pale yellow hue. These additives, while not inherently harmful in moderation, do impact the overall nutritional profile compared to cheeses with fewer added ingredients.
Comparison of Processed and Unprocessed Cheese Nutritional Profiles, 1 slice of american cheese nutrition facts
| Nutrient | American Cheese (Processed) (per ounce) | Cheddar Cheese (Unprocessed) (per ounce) |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 70-80 | 115-120 |
| Fat (g) | 6-8 | 9-10 |
| Saturated Fat (g) | 4-5 | 6-7 |
| Sodium (mg) | 170-200 | 100-150 |
| Protein (g) | 6-7 | 7-8 |
| Calcium (mg) | 150-200 | 200-250 |
| Vitamin A (IU) | Low | Moderate |
Note
These are approximate values and can vary depending on the brand and type of cheese.* It’s crucial to always check the specific nutrition label on the product you’re consuming. The table shows that while American cheese can provide some protein and calcium, it generally has a higher sodium content and lower levels of certain vitamins and minerals compared to unprocessed cheddar.
This difference highlights the impact of processing on the nutritional value.
Role in a Balanced Diet

Yo, so we’ve talked about the nutritional breakdown of a single slice of American cheese, right? Now let’s get real about how it fits (or doesn’t fit) into a balanced diet. It’s not like it’s themain* course, but it can definitely play a small part in your overall eating plan. Think of it as a supporting character, not the lead.American cheese, in moderation, can contribute a small amount of protein and calcium to your daily intake.
It’s a quick and easy source of these nutrients, which are essential for muscle growth and bone health. However, it’s also high in saturated fat and sodium, so you gotta watch out for those things. Overdoing it can throw off your healthy eating game plan.
Sodium Content and Dietary Guidelines
The high sodium content in American cheese is a big deal. Most processed cheeses are pretty salty, and that’s something to keep in mind if you’re watching your sodium intake. The recommended daily allowance of sodium is usually around 2,300 milligrams, but many health organizations suggest aiming for even lower amounts, like 1,500 milligrams, especially if you have health concerns like high blood pressure.
One slice of American cheese can contribute a significant portion of that daily limit, so you need to balance it with other low-sodium foods throughout the day. Think of it like this: if you’re already eating salty snacks and meals, adding American cheese could easily push you over the edge.
Incorporating American Cheese into Healthy Meals
Okay, so how can you actually
use* a single slice of American cheese without wrecking your diet? It’s all about portion control and smart pairings. Instead of piling it onto a burger with bacon and fries, try these ideas
A slice melted onto a whole-wheat English muffin with a side of sliced tomatoes and avocado. This adds a bit of cheesy flavor and protein without going overboard on the unhealthy stuff.Or, you could use it in a grilled cheese sandwich made with whole-wheat bread and lots of veggies like spinach and mushrooms. Again, the key is balancing it with healthier options.
Another option? A single slice atop a baked potato with a dollop of low-fat Greek yogurt instead of sour cream. The cheese adds a bit of flavor and protein, while the yogurt provides healthy fats and probiotics. It’s all about finding ways to incorporate it mindfully.
FAQ Section
Is American cheese a good source of calcium?
Yes, American cheese contains a moderate amount of calcium, contributing to daily calcium intake. However, the amount varies depending on the brand and manufacturing process.
Does American cheese contain lactose?
Yes, American cheese typically contains lactose, although the amount may be reduced during processing. Individuals with lactose intolerance may experience digestive discomfort.
How does the fat content of American cheese compare to other cheeses?
The fat content of American cheese is generally lower than that of many hard cheeses, such as cheddar, but higher than some soft cheeses like mozzarella. The specific fat content varies by brand and type.
Are there any potential health concerns associated with eating American cheese?
The high sodium content of American cheese is a primary concern for individuals watching their sodium intake. Excessive sodium consumption can contribute to high blood pressure. Regular consumption should be part of a balanced diet.










